Developing and synthesizing evidence
Introduction
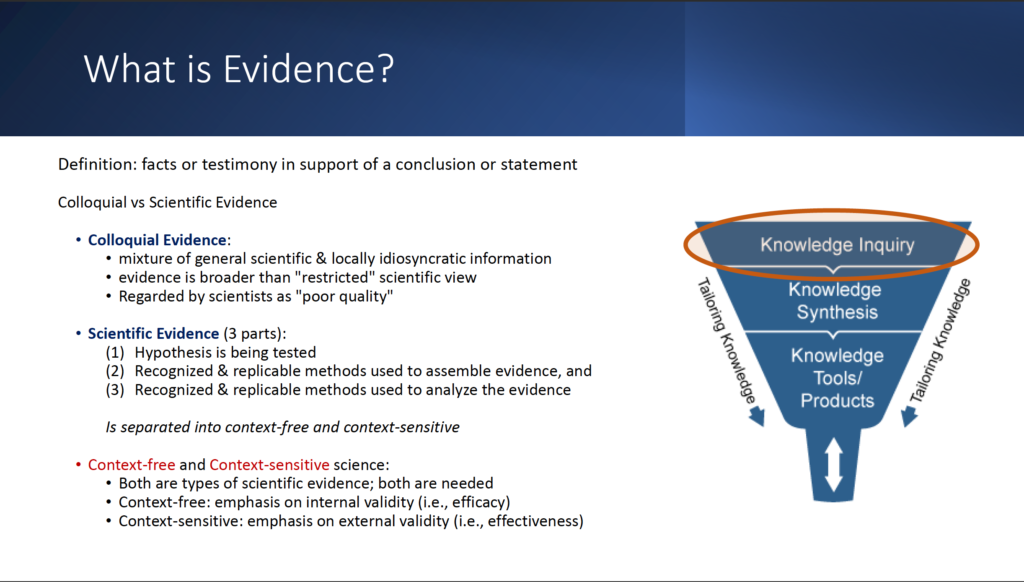
What is evidence? Evidence consists of facts or testimony in support of a conclusion or statement. Through this module, you will learn about the different types of evidence such as colloquial, context free scientific evidence and context-sensitive scientific evidence. Discover how to tailor your knowledge through ranking evidence through evaluation.
After this module, you will be able to:
- Evaluate evidence through a series of guided steps
- Define key terms related to developing and synthesizing evidence such as internal and external validity, knowledge synthesis
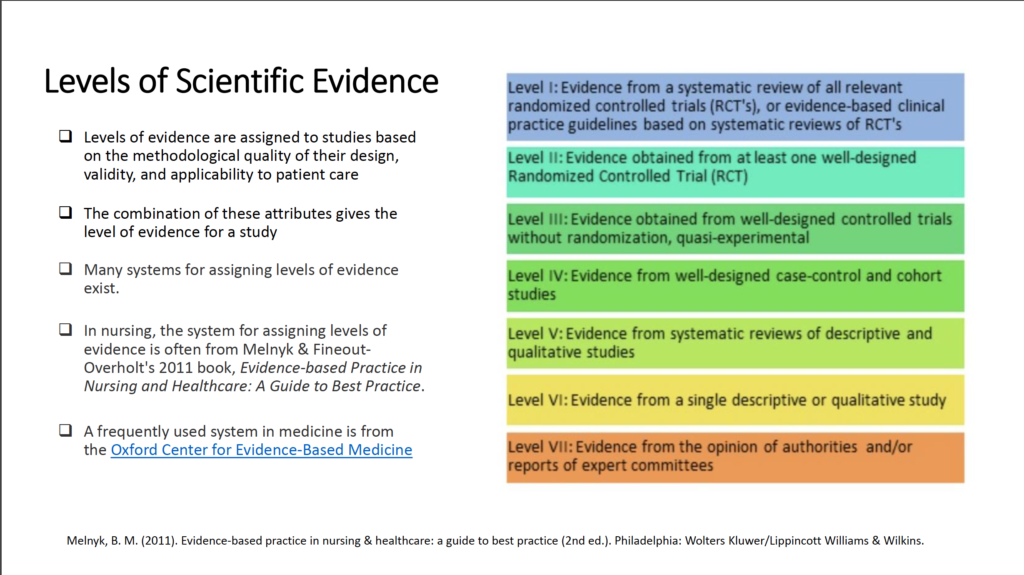
- Describe the levels of scientific evidence
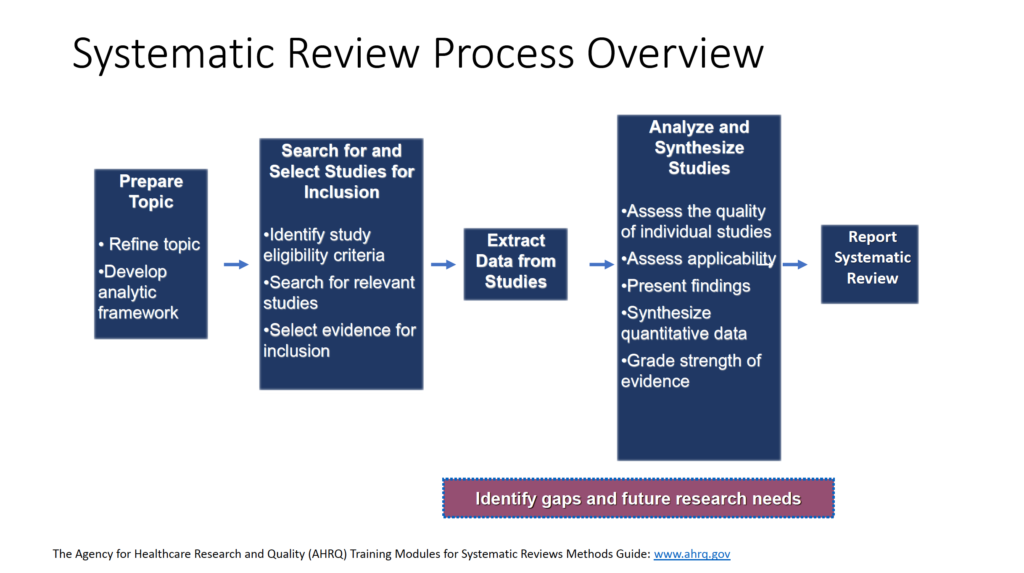
- Understand the systematic review process
- Access and use the Cochrane Library, Amstar, Health Systems Evidence
- Create knowledge tools/products such as Clinical practice guidelines, decision aids, and policy briefs
Learning Module Videos Coming Soon!

Reflective Questions
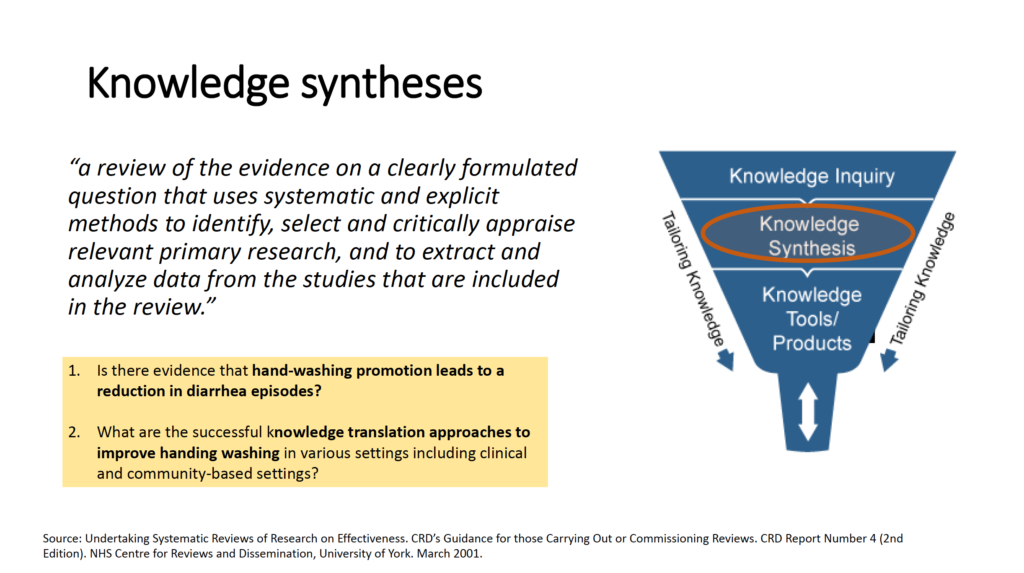
- What is knowledge synthesis?
- Why are systematic reviews at the top of the hierarchy of evidence?
- What is the difference between colloquial and scientific evidence?
- What task does each type of evidence inform: Scientific context free evidence, Scientific context sensitive evidence and Colloquial evidence?
- What questions should you ask yourself while evaluating evidence?
- What are the different levels of scientific evidence?
Resources
- The Oxford Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine (CEBM) –Critical Appraisal tools: https://www.cebm.ox.ac.uk/resources/ebm-tools/critical-appraisal-tools
- The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) Training Modules for Systematic Reviews Methods Guide: www.ahrq.gov
- The Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine: https://www.cebm.net/
- Cochrane: https://www.cochrane.org/
- Cochrane Library: https://www.cochranelibrary.com/
- Cochran EPOC: https://epoc.cochrane.org/
- Health Systems Evidence: https://www.healthsystemsevidence.org/
- AMSTAR: https://amstar.ca/index.php
- AGREE: https://www.agreetrust.org/
The Registered Nurses’ Association of Ontario: https://rnao.ca/leading-change-toolkit/more-about-the-phase-identify-the-problem
